What is Diabetes? Here are the Basics You Should Know
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition in which the body does not produce any insulin or it is where the body does not use the insulin that it does make correctly. Insulin is a hormone that is made in the pancreas and its main job is to take the sugar from the blood to the cells for energy. When there is no insulin or when there is insulin resistance present, sugar will build up in the blood stream and cause high blood sugars. Insulin is needed to take the sugar from the blood to the cells which will then bring the blood sugar back down to a normal level. If blood sugars stay high for long periods of time, complications can occur.
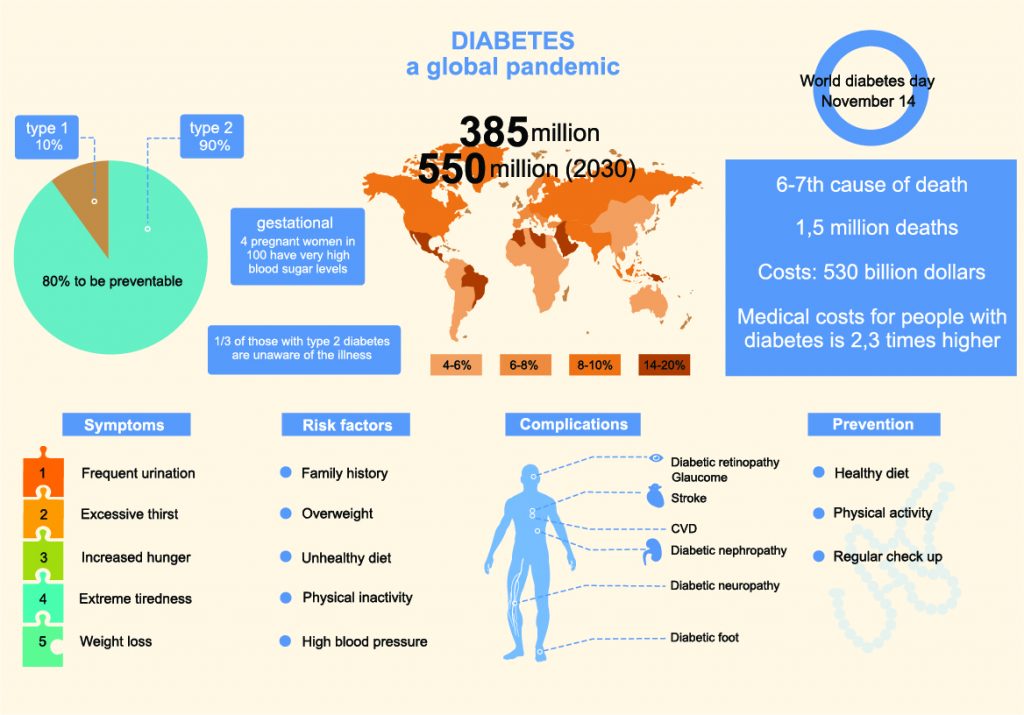
What is the difference between Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, and Gestational Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The body attacks itself and the pancreas no longer makes insulin. The patient will need insulin every day for the rest of their life and there is no cure for type 1 diabetes. A person can be diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at any age and there is no way to prevent it at this time.
Type 2 Diabetes is mainly caused by insulin resistance. The body is not using the insulin that it does make correctly. The risks for developing type 2 diabetes include family history of diabetes, being overweight, having an inactive lifestyle, over the age of 45, history of gestational diabetes, of African American, Hispanic/Latino American, American Indian or Alaskan Native, and Asian American decent. Type 2 diabetes can be controlled with diet and exercise or may require other medications to include insulin. Type 2 diabetes is on the rise and it is now being diagnosed in children and young adults as well as older adults.
Gestational Diabetes is a type of diabetes that is diagnosed during pregnancy to women that did not have diabetes prior to the pregnancy. Pregnancy causes the body to be more resistant to insulin due to the increased hormones that are present and the weight gain. The body is not able to keep up with the additional demand for insulin and elevated blood sugars occur. During the pregnancy, blood sugars and diet are monitored closely. If needed, the mother may need insulin to help control blood sugars. Once the baby is delivered, the need for additional insulin goes down and blood sugars return to normal. However, if someone has gestational diabetes, their risk for developing type 2 diabetes increases.
How do I know if I have diabetes?
The signs and symptoms may be a gradual onset with type 2 diabetes. However, with type 1 diabetes the symptoms can come on quickly.
The signs to look out for both types of diabetes are:
- increased urination
- excessive thirst
- dry mouth
- fruity breath smell
- blurry vision
- feeling very tired
- very hungry
- unexplained weight loss
- sores that do not heal
- numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- increase of infections.
Additional symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach pains
Gestational diabetes usually shows up in the middle of the pregnancy, and typically will not have symptoms. Tests are done during the 24-28th week of pregnancy to determine if a mother has gestational diabetes. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, please contact your provider to let them know.
What do I do now that I have diabetes?
Once you have been given the diagnosis of diabetes a referral is required by your physician for diabetes education. Western Missouri Medical Center has a diabetes education program that is certified by the American Diabetes Association and is accepting new patients.
The patient will have the opportunity to meet with Sherry Roberts, the Diabetes Care and Education Specialist. Sherry is a Registered Dietitian and Certified Diabetes educator and has many years of experience providing individual and group education to patients and their support system. It is her goal to come alongside the patient to provide them with a positive atmosphere in order to gain insight and knowledge to make choices to improve their overall diabetes control.
The program at Western Missouri Medical Center holds classes that review many topics pertaining to diabetes. Topics include the AADE 7- Self Care Behaviors, nutrition and carb counting, reducing risks, and heart health with diabetes. Please do not hesitate to reach out to Sherry Roberts RD, LD, CDE for additional information at (660) 262-7717 or by contacting us here.
To learn more about WMMC, visit WMMC.com/ProviderFinder to see a complete list of providers and services.
Author: Sherry Roberts RD, LD, CDE
Other Recent Posts by WMMC:
Warrensburg Express Care Extending Hours and Coverage
WMMC to Host 2nd Annual Baby Shower and Reunion
Dennis’ Story: My Partner for Fast Stroke Care
About Western Missouri Medical Center
Western Missouri Medical Center (WMMC) is a fully-accredited acute care county medical center located in Warrensburg, MO. WMMC prides itself in emergency care, obstetrics, orthopedic and general surgery, family healthcare, internal medicine, outpatient clinics, ambulatory care, rehabilitation services and more. Inpatient services include medical, surgical, intensive, obstetrical, orthopedic, pediatric and skilled nursing care, as well as a wide range of therapeutic and diagnostic outpatient servics. This institution is an equal opportunity provider and employer. Learn more at WMMC.com
